ADD vs ADHD Disorder Overview
One form of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is called “attention deficit disorder,” or ADD. Problems with paying attention in class, staying on task, finishing homework, and interacting socially are some of the behavioral issues that can arise from the neurological disorder known as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
What is Attention Deficit Disorder?
Although the term attention deficit disorder (ADD) is now considered archaic by medical professionals, it is still commonly used to refer to a person with a subtype of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) known as predominantly inattentive ADHD.
What are the Differences Between ADD and ADHD?
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are problems with paying attention, but they are different. Here are the main ways in which ADD and ADHD are different:
Attention and Hyperactivity Levels
- ADD: People with ADD mostly have trouble paying attention, staying on task, being easily distracted, and getting things done.
- ADHD: People with ADHD have trouble paying attention, are hyperactive, and act impulsively. They might be restless, talk too much, move around, and have trouble sitting still.
Diagnostic Terminology
- ADD: The term “ADD” is often used to mean ADHD, predominantly inattentive type, which is a type of ADHD. It focuses on symptoms that have to do with paying attention.
- ADHD: is a broader term that includes not paying attention and being too active or impulsive.
Diagnostic Criteria
- ADD: Symptoms of inattention, such as having trouble staying focused, forgetting things, and being disorganized, are usually used to diagnose ADD.
- ADHD: Symptoms of not paying attention and being too active or impulsive are used to diagnose ADHD. To meet the diagnostic criteria, a person must have more than one of these symptoms.
Perception of Internal Restlessness
- ADD: People with ADD may feel restless inside, but they may not show it on the outside. They might seem to be daydreaming or “in their own world.”
- ADHD: People with ADHD often show signs of restlessness and hyperactivity to the outside world, like being on the go all the time, fidgeting, or talking too much.
Thoughts on Treatment
- ADD: Behavior interventions, counseling, and support are used to help people with ADD who are having trouble paying attention.
- ADHD: Attention and hyperactivity/impulsivity problems need to be fixed to treat ADHD. In addition to changing how people act, medications may also be used to control symptoms.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Types & Treatments
- Postpartum Depression Treatment. Symptoms, Causes, and Risks.
- Mood Disorders Symptoms, Causes & Treatments
- Anxiety Treatment, Therapies, CBT, Medications, Anxiety Disorder Symptoms, Phobia-Related Disorders & Separation Anxiety Disorder
- Psychiatric Disorders, Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatment
Symptoms of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Since ADD and ADHD are simply different manifestations of the same condition, there is considerable overlap in their presenting symptoms. The most widely recognized signs and symptoms of each are:
ADD Symptoms:
- Inattention or carelessness.
- Trouble concentrating.
- Distracted easily.
- Organizational issues.
- Aversion to mental labor.
- Problems with instructions or assignments.
- Forgetfulness or losing things.
- Being easily overwhelmed by tasks or information.
- Daydreaming or appearing “in a world of their own.”.
ADHD symptoms:
- Hyperactivity: Constant movement, fidgeting, and squirming.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, interrupting, blurting out answers, difficulty waiting their turn.
- Trouble sitting, especially in situations that require stillness.
- Talking too much without thinking about others.
- Trouble waiting or delaying gratification.
- Trouble following directions.
- Risk-taking without considering the consequences.
- Emotional instability causes mood swings or irritability.
- Symptoms vary by person. A medical or mental health professional should diagnose based on symptoms, history, and functioning.
Types of ADHD
There are three different types of ADHD, depending on which types of symptoms are strongest in the individual:
- Predominantly Inattentive Presentation: It is hard for the individual to organize or finish a task, pay attention to details, or follow instructions or conversations. The person is easily distracted or forgets details of daily routines.
- Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation: The person fidgets and talks a lot. It is hard to sit still for long (e.g., for a meal or while doing homework). Smaller children may run, jump or climb constantly. The individual feels restless and has trouble with impulsivity. Someone impulsively interrupts others, grabs things from people, or speaks at inappropriate times. It is hard for the person to wait their turn or listen to directions. A person with impulsiveness may have more accidents and injuries than others.
- Combined Presentation: Symptoms of the above two types are equally present in the person.
When Does Normal Behavior Become Attention Deficit Disorder (ADHD)?
At some point in their lives, nearly everyone experiences symptoms that are similar to ADHD. You probably don’t have ADHD if your problems are new or have only happened rarely. To receive a diagnosis of ADHD, symptoms must be severe enough to impair daily functioning in more than one area of life. These bothersome symptoms have been around since they were young children.
Due to the similarities between ADHD symptoms and those of other conditions, such as anxiety and mood disorders, a correct diagnosis of ADHD in adults can be challenging. Additionally, many adults who have ADHD also suffer from other mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety.
Does Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in adults look different?
Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder may experience symptoms differently compared to children. While some symptoms may persist from childhood into adulthood, there are also unique challenges that adult ADD faces. Here are some key considerations:
- Recognition and Diagnosis: ADHD symptoms in adults can be overlooked or misattributed to other causes. Inattentive, less disruptive, and more internal symptoms may go unrecognized, especially in girls and women. This can result in a delayed diagnosis or individuals seeking support only when encountering difficulties in various areas.
- Improved Coping Skills: With age, individuals with ADHD may develop better-coping mechanisms and strategies to manage their symptoms. However, these skills may not be effectively utilized without proper diagnosis and treatment, leading to ongoing challenges.
- Impact of Responsibilities: ADHD and ADD in adults often have increased responsibilities in various domains of life, such as work, relationships, and finances. This can amplify the impact of ADHD symptoms. Difficulties with organization, time management, and impulsivity can have more significant consequences, affecting job performance, financial stability, and interpersonal relationships.
- Co-occurring Mental Health Conditions: Adults with ADHD may also experience co-occurring mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. These conditions can interact with ADHD symptoms, exacerbating challenges and affecting overall well-being.
- Environmental and Life Factors: Stressors and demands in adulthood, such as career pressures, financial obligations, and relationship dynamics, can contribute to changes in ADHD symptoms. Increased stress levels and demanding environments may make it more difficult to manage symptoms effectively.
Attention Deficit Disorder Facts
Overview
Attention deficit disorder (ADD) is an outdated term for what experts now call attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The term ADD first appeared in the third edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-3), a reference manual that helps mental health professionals diagnose mental health conditions. Experts separated the condition into two subtypes. ADD with hyperactivity and ADD without hyperactivity.
ADD vs ADHD Etiologic Theories
Neurobiological factors appear to play a role in the onset of ADD. Studies of twins and adoptions offer strong evidence of a genetic link, and 20% of parents of children with ADD have the problem themselves. People with ADD might have problems in the prefrontal cortex that would affect dopamine and noradrenaline levels and structural changes in the striatum and the cortex.
ADHD Diagnosis
ADHD is a disorder that is diagnosed clinically and does not have any specific laboratory or radiologic tests. The neuropsychological tests are not as sensitive for diagnosing the disorder; hence, the disorder should be diagnosed based on the patient’s history.
The evaluation of the patient with ADHD is usually done with different rating scales and multiple informants, who may include the teachers and parents. A clinician must look for other disorders that may cause a person’s symptoms. It should not be diagnosed in the context of symptoms from another disorder, for example, a psychotic episode or manic episode.
ADD vs ADHD Comorbidity
Half of those with ADD have comorbid psychiatric disorders: 19% to 37% have mood disorders (depression, bipolar affective disorders, and dysthymia), 25% to 50% have anxiety disorders, 32% to 53% have addiction problems, and 10% to 28% have personality disorders. This comorbidity is why the diagnosis is often missed, even though the comorbid problems are
ADHD Pathophysiology
ADHD is associated with cognitive and functional deficits related to diffuse abnormalities in the brain. The anterior cingulate gyrus and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLFPC) are found to be small in individuals who are suffering from ADHD.
These changes account for the deficits in goal-directed behavior. Moreover, activity in the frontostriatal region is also reduced in these individuals as measured by fMRI. It is important to understand these pathophysiological mechanisms so that pharmacotherapy is directed toward them.
End the Emotional Pain. Get Your Life Back.
Feeling Depressed, Anxious or Struggling with Mental Health Illness? Get Safe Comfortable Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Therapy From Counselors That Care. Begin Your Recovery Now.
Hotline: (509) 348-4077

ADD vs ADHD Disorders Statistics
When the American Psychiatric Association released a revised edition in 1987, they combined these two subtypes into one condition, ADHD. Adults can have ADHD too. Nearly 2.6 percent of adults globally have persistent ADHD from childhood, while about 6.7 percent of adults have symptoms of adult ADHD.
1 in 5
In 2020, Nearly one in five U.S. adults lived with a mental illness. The most common mental disorders in the US are anxiety, major depression, and bipolar disorder.
Source: NIMH
8.7 Million
In 2019, the number of visits to physician offices with attention deficit disorder as the primary diagnosis was 8.7 million.
Source: NIMH
9.5%
Approximately 9.5% of American adults, ages 18 and over, will suffer from a depressive illness (major depression, bipolar disorder, or dysthymia) each year.
Source: NIMH
How ADHD is Diagnosed, ADHD vs ADD Test
The following are typical steps in any assessment process:
- Clinical Interview: The healthcare provider will ask in-depth questions about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history, among other things.
- Rating Scales and Questionnaires: ADHD symptoms can be measured with standardized rating scales and questionnaires. Individuals’ parents, teachers, and other influential people who have observed their behavior may also fill out these instruments.
- Diagnostic Criteria: The health care professional will compare the person’s symptoms and how well they are doing with the diagnostic criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Predominant inattentive, hyperactive/impulsive, and combined are the three subtypes of ADHD.
- Medical Exam: A physical exam may be done to rule out any underlying health problems that might be causing the symptoms.
WARNING: no online quiz or self-test can give you a firm diagnosis of ADHD or ADD. They could be useful for quick screening, but a proper diagnosis requires the expertise of a medical professional.
ADHD vs ADD Infographic
While predominantly inattentive ADHD is a subtype of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), the term attention deficit disorder (ADD), once used to describe it, is now regarded as archaic by medical professionals.
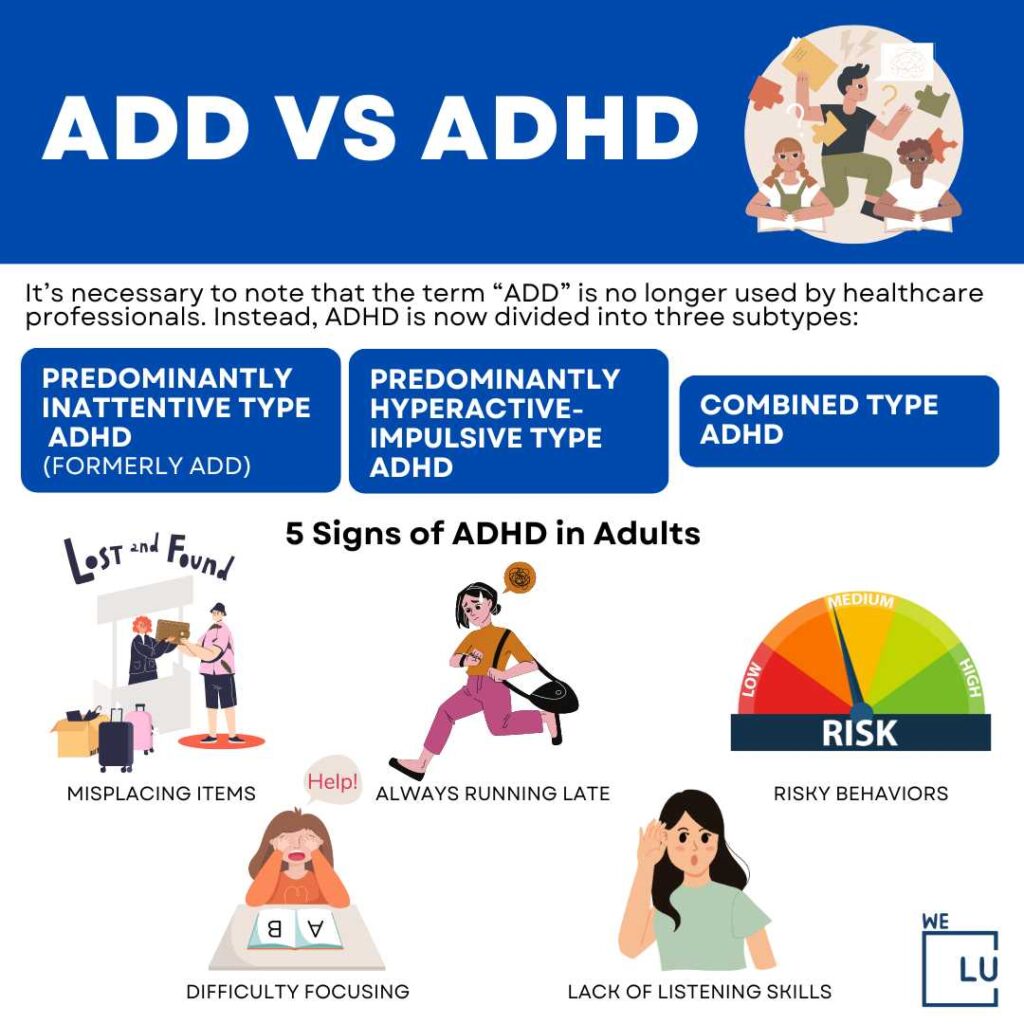
Embed the above “ADHD vs ADD” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupwa.com/mental-health/attention-deficit-disorder/
ADHD vs ADD image link: https://welevelupwa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/ADD-vs-ADHD-1024×1024.jpg

Embed the above “Inattentive ADHD” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up addiction treatment center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupwa.com/mental-health/attention-deficit-disorder/
Inattentive ADHD image link: https://welevelupwa.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Inattentive-ADHD-1024×1024.jpg
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Centers Near You?
Even if therapy failed previously, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about counseling alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE 24/7 Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Services HotlineWhen to See a Doctor For Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Medication (ADD Medication)
Talk to your doctor about possible ADHD if any of the symptoms listed in the article are a persistent problem for you.ADHD can be diagnosed and treated by a wide range of medical professionals. Find a doctor who has experience treating adults for ADHD.
If you think you have Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and are considering using medication to treat it. We Level Up WA (Washington) is a good option to consider when the following symptoms warrant medical attention and ADD medication evaluation:
- Suppose inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity have been causing significant problems in your daily life, at work, with your relationships, or overall well-being. In that case, it may be time to consult a professional.
- If you’re having trouble at work or school, if your responsibilities are piling up, if your relationships are deteriorating, or if you’re falling short of your personal goals, it’s time to consider getting help for your ADHD.
- Suppose you have tried non-medication interventions like therapy or lifestyle changes for managing your ADHD symptoms in the past and have not seen significant improvement. In that case, your doctor may recommend trying medication.
Medication may be considered part of a comprehensive treatment plan for those who also suffer from co-occurring mental health conditions like anxiety or depression, which can have a multiplicative effect on the severity of ADHD symptoms.
Comfortable Facilities & Amenities
High-Quality Mental Health Services & Behaviroal Health Substance Abuse Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Mental Health Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient Rehab Programs Vary.
Mental Health Helpline: (509) 348-4077Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Development Events
- Comfortable Onsite Medical Detox Center
ADHD and ADD Medication
Psychostimulants, antidepressants, and non-stimulant drugs are the three most common types of ADHD or ADD medication. This medication for anxiety and ADD has shown promise in helping people with inattentive ADD maintain focus and attention.
Psychostimulants: Psychostimulants impact neurotransmitters in the brain, which may help ADD patients with anxiety feel more energized and attentive. The extended-release form (rather than the immediate-release form) is typically advised. Amphétamines like Adderall (Adderall for ADD vs ADHD) and methylphenidates like Ritalin and Concerta are two examples of psychostimulants.
Antidepressants: Antidepressants also affect neurotransmitters in the brain, so they may help those with adult ADD and anxiety improve their mood and focus. Common antidepressants for ADHD inattentive symptoms include Wellbutrin (bupropion) and Effexor (venlafaxine).
Non-stimulant drugs: For some who experience undesirable stimulant side effects, ADD medicines can be beneficial. Strattera (atomoxetine) and Intuniv (guanfacine) are prescribed for anxiety and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, respectively. Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that non-stimulants may affect and is used for emotional regulation and task improvement.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Mental Health Dual Diagnosis Programs. Complete Integrated Inpatient Rehab with Free Post Discharge Therapy Planning.
Hotline: (509) 348-4077End the Emotional Pain Rollercoaster. Gain Stability & Happiness Through Recovery Treatment. Start Mental Health Counseling Today. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Behaviroal Health Specialists Who Understand Mental Health Recovery.
Best ADD Medication for Adults with Anxiety
ADHD and ADD share some symptoms but are otherwise distinct disorders. Hyperactivity is not a symptom of attention deficit disorder (ADD). Modern diagnostic criteria lump ADD’s symptoms together with those of inattentive ADHD rather than listing ADD as a distinct disorder. Individuals diagnosed with ADHD or ADD may struggle in school and later in life.
Once a doctor has made an accurate diagnosis, treatment may include diet, exercise, and medication advice. Seeking medical attention is a good idea if any of the aforementioned symptoms prevent the individual from succeeding academically, professionally, or relationally.
Medication and therapy sessions are commonly used to treat adult ADHD and ADD. The best place to begin treatment will depend on the severity of your symptoms. Treating the underlying cause of a secondary mental health condition can help alleviate symptoms of the primary disorder.

- ADHD is often treated with stimulants that boost brain chemicals linked to focus and thinking. They can help with symptoms while you’re at school or work but can also make you less hungry or cause headaches or sleep problems.
- Some ADHD drugs don’t involve stimulants or have the same side effects. But they may not work as quickly. Your doctor might give you a combination of stimulants and non-stimulant drugs.
- Living with the symptoms of ADD vs ADHD in adults can be challenging, but you can take steps to manage both conditions. A mental health professional may prescribe stimulant and antidepressant medications. They may also recommend counseling or other therapies.
Our Washington State mental health center, We Level Up WA, features an ADHD treatment program. Clients engage in clinical and experiential modalities as part of our rounded program. We can help your loved one diagnosed with ADHD learn more about the condition and develop the coping mechanisms to allow them to thrive.
Popular Attention Deficit Disorder FAQs
-
Is attention deficit disorder a disability?
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), also known as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), can be considered a disability. ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects a person’s ability to pay attention, control impulses, and regulate behavior. It can impact various areas of life, including academics, work, relationships, and daily functioning.
-
Is attention deficit disorder a mental illness?
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), is considered a mental illness.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired.
Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to a behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Search We Level Up WA / Detox & Mental Health Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) vs Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Symptoms, Diagnosis, & Treatments Topics & Resources
Sources
[1] What is ADHD? | CDC Examining ADD vs ADHD
[2] NIMH » Mental Illness (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Review
[3] NIMH » Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) (nih.gov)
[4] Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Adults Review.
[5] ADHD: Reviewing the Causes and Evaluating Solutions – PMC (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD in Adults Causes.
[6] What is mental health? Evidence towards a new definition from a mixed methods multidisciplinary international survey – PMC (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Symptoms
[7] COMMON MENTAL HEALTH DISORDERS – Common Mental Health Disorders – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD in Female Adults
[8] About Mental Health (cdc.gov)
[9] Information about Mental Illness and the Brain – NIH Curriculum Supplement Series – NCBI Bookshelf
[10] Effective Mood And Personality Disorder Treatment (welevelupnj.com)